Lab 1 - Alarm Multi-Blink
MCU Timer Based Interrupts
Summary
Create a classic 'hello world' LED blinker, then change it to run using interrupts & control multiple LEDs.
1. build a basic 'hello world' project using cpu sleep to control blinking.
2. alter the project to use an alarm function that calls itself instead of cpu sleep timing.
3. add 2-3 more external LEDs that all blink at different rates using alarm functions.
Required Equipment and Supplies
- Rasperry Pi Pico with Headers - pinout diagram
- LED - indicator [x3]
- 820Ω Resistor [x3]
- USB Micro Cable
- Breadboard
- Cables and 22ga wire as needed
Wiring
- Only begin adding external LEDs after your basic blink and alarm blink are working.
- LEDs consume very little power, you may power everything from the USB cable.
- Use VBus or Vsys to supply your breadboard power rail from the Pi Pico.
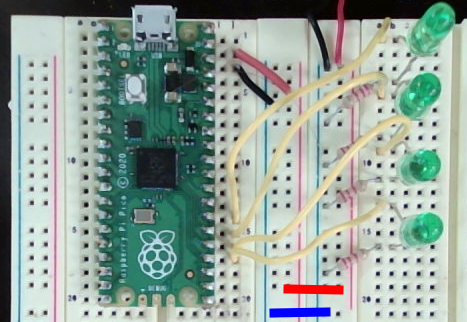
- Connect each LED to separate GPIO pin and in series with a current limiting resistor connected to ground like the example below.
Sample Code - CPU Timed Blink
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
int main() {
// setup and initialize
gpio_init(25);
gpio_set_dir(25, GPIO_OUT);
// primary loop
while (true) {
gpio_put(25, 1);
sleep_ms(500);
gpio_put(25, 0);
sleep_ms(500);
}
}
Sample Code - Single Alarm Timed Blink
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
uint led_pin = 25;
bool led_state = false;
int64_t led_delay_ms = 500ll;
alarm_callback_t alarmStuff(alarm_id_t id, void* user_data){
//what our alarm will do when it triggers.
led_state = !led_state;
gpio_put(led_pin, led_state);
int64_t reschedule_micros = led_delay_ms*-1000ll;
return reschedule_micros;
}
int main() {
// setup and initialize
gpio_init(led_pin);
gpio_set_dir(led_pin, GPIO_OUT);
gpio_put(led_pin, 0);
//set an alarm
add_alarm_in_ms(3000, alarmStuff, NULL, true);
// primary loop
while (true) {
sleep_ms(250);
}
}
Sample Code - Alarms Multi Blink
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
const uint LED_1 = 18;
const uint LED_2 = 19;
const uint LED_3 = 20;
const uint LED_4 = 21;
bool led_1_state = true;
bool led_2_state = true;
bool led_3_state = true;
bool led_4_state = true;
int64_t led1_delay = 61ll;
int64_t led2_delay = 294ll;
int64_t led3_delay = 167ll;
int64_t led4_delay = 83ll;
int64_t alarm_call_led1(alarm_id_t id, void* userdata) {
led_1_state = !led_1_state;
gpio_put(LED_1, led_1_state);
int64_t reschedule_micros = led1_delay * -1000ll;
// multiply by 1000 to convert to microseconds
// make sure to usea 64bit integer types - long long
// literal values need two lower-case 'l' characters at the end
return reschedule_micros;
}
int64_t alarm_call_led2(alarm_id_t id, void* userdata) {
led_2_state = !led_2_state;
gpio_put(LED_2, led_2_state);
int64_t reschedule_micros = led_delay * -1000ll;
// multiply by 1000 to convert to microseconds
// make sure to usea 64bit integer types - long long
// literal values need two lower-case 'l' characters at the end
return reschedule_micros;}
int64_t alarm_call_led3(alarm_id_t id, void* userdata) {
led_3_state = !led_3_state;
gpio_put(LED_3, led_3_state);
int64_t reschedule_micros = led3_delay * -1000ll;
// multiply by 1000 to convert to microseconds
// make sure to usea 64bit integer types - long long
// literal values need two lower-case 'l' characters at the end
return reschedule_micros;}
int64_t alarm_call_led4(alarm_id_t id, void* userdata) {
led_4_state = !led_4_state;
gpio_put(LED_4, led_4_state);
int64_t reschedule_micros = led4_delay * -1000ll;
// multiply by 1000 to convert to microseconds
// make sure to usea 64bit integer types - long long
// literal values need two lower-case 'l' characters at the end
return reschedule_micros;}
int main() {
// setup and initialize
gpio_init(LED_1);
gpio_set_dir(LED_1,led_1_state);
gpio_put(LED_1, 1);
gpio_init(LED_2);
gpio_set_dir(LED_2,led_2_state);
gpio_put(LED_2, 1);
gpio_init(LED_3);
gpio_set_dir(LED_3,led_3_state);
gpio_put(LED_3, 1);
gpio_init(LED_4);
gpio_set_dir(LED_4,led_4_state);
gpio_put(LED_4, 1);
//delay for verification
sleep_ms(1000);
add_alarm_in_ms(led1_delay,alarm_call_led1, NULL, true);
add_alarm_in_ms(led2_delay,alarm_call_led2, NULL, true);
add_alarm_in_ms(led3_delay,alarm_call_led3, NULL, true);
add_alarm_in_ms(led4_delay,alarm_call_led4, NULL, true);
// primary loop
while (true) {
sleep_ms(500);
}
}
Sample Code - Single Alarm Callback with Custom Data Structure
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
//Notes: Each blinking light needs
// -Pin number, -state bool, time on, time off
typedef struct Blinking_LED_t {
uint pin;
bool state;
int onMicros;
int offMicros;
} Blinking_LED_t;
void setup_blinking_led(Blinking_LED_t* led, int pin_no, int onDelay, int offDelay);
int64_t blink_alarm_callback(alarm_id_t id, void *user_data);
int main() {
// setup & initialize a single led struct var and set its alarm
Blinking_LED_t test_led;
setup_blinking_led(&test_led, 25, 50000, 200000);
add_alarm_in_us(20000, blink_alarm_callback, &test_led, true);
Blinking_LED_t ext_leds[3];
int pin_numbers[] = {0,1,2};
int on_delays[] = {150000, 20000, 400000};
int off_delays[] = {37000, 100000, 83000};
//setup for the entire array
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
setup_blinking_led(&ext_leds[i], pin_numbers[i], on_delays[i], off_delays[i]);
add_alarm_in_us(20000,blink_alarm_callback, &ext_leds[i], true);
}
// primary loop
while (true) {
sleep_ms(10);
}
}
int64_t blink_alarm_callback(alarm_id_t id, void *user_data){
//note user_data is a void pointer or unknown data type pointer
// we change it's data type to our struct here.
Blinking_LED_t* led = (Blinking_LED_t*)user_data;
//toggle the state
led->state = !(led->state);
//set the pin voltage
gpio_put(led->pin, led->state);
if(led->state){
//on cycle
return led->onMicros;
} else {
//off cycle
return led->offMicros;
}
}
void setup_blinking_led(Blinking_LED_t* led, int pin_no, int onDelay, int offDelay) {
//set the values in the led struct variable we were given.
led->pin = pin_no;
led->onMicros = onDelay;
led->offMicros = offDelay;
led->state = false;
// setup the pin physically
gpio_init(led->pin);
gpio_set_dir(led->pin, GPIO_OUT);
gpio_put(led->pin, 0);
}